Diary of a Freight Forwarder
#
- 3461 Form (Immediate Delivery) – A form submitted to U.S. Customs by a customs broker to expedite the initial examination and release of goods. It is also referred to as the “customs release” form.
- 3PL – Also known as third-party logistics—refers to companies that contract with a specialized provider to handle logistics tasks like fulfillment, transportation, and warehousing.
- 5104 Form (Create/Update Importer Identity) – A form used in the CBP system to create or update an importer’s unique identity information.
- 7501 Form (Entry Summary) – A crucial document that CBP requires for importing goods into the United States, serving as the official declaration of imported merchandise and providing the basis for duty assessment.
- 7512 Form (Transportation Entry and Manifest of Goods Subject to CBP Inspection and Permit) – A form used when goods are transported from the airport or port of arrival to another location intended for exportation to another country.
A
- Air Waybill (AWB) – A shipping document that acts as a contract between the shipper and an airline.
- Airport Terminal Fee – A service a ground handler provides to unload goods from the aircraft at an airport.
- Airport Transfer – A transportation service from a consolidation warehouse that performs export cargo inspection to an airport terminal.
- All-Risk Insurance Coverage – This insurance offers the broadest and most complete coverage, protecting against almost any physical loss or damage to cargo during transit from any external cause except for those expressly excluded in the policy.
- Anti-Dumping Duties (AD) – A tax on imported goods sold for less than their usual worth. This duty lessens the likelihood of unfair competition for domestic industries.
- Automated Export System (AES) – A system used to gather, process, and store electronic export information from individuals or companies who export products from the U.S., Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
- Automated Manifest System (AMS) – An electronic system that facilitates the processing of cargo shipments by U.S. Customs to expedite the customs clearance procedure and reduce the need for paper records.
B
- Bill of Lading (BOL or B/L) – An essential document that describes the details of a shipment and the obligations of the parties involved. It serves as a receipt, contract of carriage, and proof of ownership for the goods being transported.
- Blank Sailing – When an ocean carrier cancels or skips a scheduled port stop due to poor weather, strikes, or to manage vessel capacity according to demand.
- Blind Shipment – This shipping method conceals the original shipper's or supplier's identity from the final recipient to give the distributor a competitive edge by shipping directly from the manufacturer to the end user.
- Block & Brace – A method used to hold cargo inside a container or trailer to stop movement and damage during transit, ensuring safe and intact delivery of the shipment.
- Bonded Cargo – Imported goods that have not yet paid taxes or customs duties.
- Bonded Shipment – A shipment that passes through one or more countries without going through customs clearance until it reaches its final destination.
- Bunker Adjustment Factor (BAF) – A fuel surcharge added to shipping rates to account for fluctuations in fuel prices. Also known as a bunker surcharge.
C
- Cargo Consolidation – The process of combining several small orders from multiple shippers into a single and bigger shipment to maximize costs and efficiency.
- Cargo Insurance – Protects shipments from loss, damage, or theft during transit, whether a covered incident occurs by land, air, or sea.
- Cargo Insurance Coverage Limits – Limitations that specify the maximum amount an insurer will pay for loss or damage to goods during transit. These limits are usually expressed as a dollar amount or percentage of the good’s value.
- Cargo Owner Liability Coverage – A type of insurance required by the carrier that shields the insured from third-party claims alleging their cargo caused property damage, personal injury, or death during transit.
- Cargo Ready Date (CRD) – The date when goods are prepared and ready to be picked up from the supplier and turned over to a logistics provider.
- Centralized Examination Station (CES) – A privately run facility where shipping goods are made available to customs officials for physical inspection.
- Certificate of Origin – A document that confirms the country in which a product was produced, processed, or grown to determine any applicable duties and ensure compliance with trade agreements.
- Chargeable Weight – The weight used to determine the shipping cost by comparing the actual weight versus the volumetric (dimensional) weight and using the higher value for billing purposes.
- Chassis – A metal frame with wheels attached to a truck to transport ocean containers between ports, rail ramps, or warehouses.
- Chassis Split – When a trucker must pick up or drop off a chassis somewhere other than where the container was picked up or delivered. This results in a driver traveling to two different locations to retrieve both the container and the chassis, thus incurring a fee.
- Co-Loader – A logistics provider that consolidates cargo from several shippers into a single container, increasing cost-effectiveness and optimizing space utilization for LCL shipping services.
- Commercial Control List (CCL) – A list managed by the Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) that identifies goods that are subject to export controls and require licenses to prevent the misuse of sensitive products, software, and technology.
- Commercial Invoice – An essential document for international shipping that acts as a customs declaration and gives information about the products being shipped, their value, and the transaction between the buyer and the seller to allow customs officers assess duties and taxes.
- Common Carrier – An enterprise that charges for the transportation of people or products and declares that its services are available to the general public.
- Consignee – A person or business that receives the imported goods and takes ownership upon receiving them.
- Container Freight Station (CFS) – A logistics facility where LCL cargo is consolidated and deconsolidated before being shipped.
- Container Yard Cutoff – A deadline, determined by the carrier and typically 2 days before the next sailing, by which containers must be checked into the port terminal to be loaded onto the scheduled vessel.
- Continuous Bond – A financial guarantee that covers several import shipment transactions over an annual period and automatically renews until cancelled, guaranteeing payment of duties and fees to U.S. Customs.
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) – An agreement between governments to control the international trade of endangered plants and animals and prevent overexploitation of these species to ensure their survival in the wild.
- Country of Origin Marking – A mandatory requirement for goods that are imported and sold in the U.S. market, indicating their country of origin.
- Courier Service – A shipping method where a courier picks up small or medium-sized packages, usually weighing less than 75 lbs., from a sender’s address and delivers them directly to the recipient’s location.
- Customs Assigned Importer Number (CAIN) – A special number that importers are given by the U.S. Customs to monitor imports and guarantee compliance with regulations.
- Customs Bond – A financial guarantee or surety bond to make sure importers comply with customs regulations and pay all tariffs, taxes, and related fees.
- Customs Broker – A licensed individual or business that serves as a liaison between importers and customs authorities, facilitating the clearance of goods by handling the paperwork, ensuring compliance with regulations, and paying duties and taxes.
- Customs Clearance – A mandatory process for bringing goods into or out of a country involving a customs declaration, inspecting goods, paying duties and taxes, and allowing shipments to proceed to their destination.
- Customs Exam – A process where imported products are examined to make sure they comply with U.S. rules and regulations, including verifying the accuracy of description and detecting possible violations such as unlawful or contraband goods.
- Customs Valuation – A process of figuring out the commercial value of goods to calculate duties, taxes, and other related fees.
- Customs Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT) – A public-private partnership program that is a vital component of U.S. Customs and CBP, serving as a critical multi-layered security strategy. Through this initiative, CBP collaborates with the trade community to enhance U.S. border security and global supply networks.
D
- Debris Removal – A service that removes and disposes of any packaging materials from the unloading and handling of cargo.
- Deconsolidation – A service that entails breaking down a large and consolidated shipment into smaller pallets or packages for distribution to multiple destinations.
- Demurrage – A charge imposed to the consignee or shipper for keeping the container at the port, rail ramp, or terminal beyond the agreed-upon free time, encouraging quicker cargo movement and container turnover.
- Detention – A charge imposed to the consignee or shipper for holding the container longer than the allowed free time outside the port, rail ramp, or terminal.
- Devanning – The process of unloading cargo out of a sealed container at an assigned warehouse.
- Disbursement Fee – A charge imposed by a freight forwarder to help the shipper or consignee pay for duties and taxes on their behalf.
- Drayage – The transportation of containerized cargo from a port, rail ramp, or terminal to a short-distance destination.
- Drop-off Container – A trucking delivery service involving a driver dropping off a container at the unloading site and departing without waiting for the container to be emptied and returning on a different day to pick up the empty container.
- Dry Run – A fee imposed on the shipper or consignee when a driver arrives either at the pickup or delivery site and the cargo is unavailable, not ready, or it cannot be completed for some other reason.
- Dry Van – A trailer that handles dry freight rather than temperature-controlled perishable goods.
- Duty – A tax or tariff that is applied to commodities as they cross international borders, primarily to protect local industries and generate revenue for the importing country.
- Duty Drawback – A refund of taxes, customs charges, and other fees paid on imported goods that are later exported or destroyed.
E
- Electronic Export Information (EEI) – An electronic declaration of products departing the U.S. for exports when their commercial value exceeds $2,500 (per schedule B number).
- Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) – A five-character alphanumeric code used by the U.S. Department of Commerce to identify and classify goods that are subject to export control restrictions and to help determine if an export license is required.
- Export Declaration – A document that includes comprehensive information on items being exported from one country to another.
- Export License – A government-issued document that permits the shipping of certain products to a given destination for a designated end use and ensuring compliance with export regulations.
- Express Bill of Lading – A type of Bill of Lading that allows for a faster cargo release to the consignee by removing the requirement of presenting an original bill of lading and expediting the shipping procedure.
F
- FBA ID – A unique identifier number given to shipments handled by Amazon’s FBA program that is used to monitor orders and inventory.
- Flatbed Truck – A large vehicle with a flat body and no roof or sides around the bed that transports heavy loads that would be too wide for an enclosed-body truck.
- Flatrack Container – A type of container with a flat open bed and collapsible walls that is specifically used to carry large, bulky, or unusually shaped cargo that would not fit in a typical container.
- Forklift – A self-propelled equipment that uses steel fingers inserted beneath the cargo to lift and move heavy pallets or crates.
- Free Trade Zone (FTZ) – A specific location where goods can be landed, stored, handled, and then re-exported without incurring customs charges until they are taken out of the FTZ for domestic consumption.
- Fuel Surcharge (FSC) – An additional cost applied to the shipping rate to cover variable fuel costs, ensuring carriers can manage unpredictable, volatile fuel prices and continue to be profitable.
- Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) – A service where Amazon manages the storage, packaging, and shipping for products sold by independent sellers on the Amazon marketplace.
- Full Container Load (FCL) – A shipment that fills the entire space inside a container, sealed at origin, and delivered straight to its destination without sharing space with other shippers.
- Full Truck Load (FTL) – A shipment for a single customer that fills a truck or trailer to its capacity.
G
- Gating In – A process where a container enters a port, rail ramp, or terminal, which includes checking in, confirming paperwork, and ensuring compliance before it is permitted to enter the assigned area for handling and storage.
- General Average – A maritime law principle where all parties involved in a voyage split losses and costs resulting from a voluntary sacrifice to protect the ship and its cargo from a shared peril.
- General Rate Increase (GRI) – A planned increase charge for certain trade routes that shipping lines implement to accommodate changing market conditions or growing costs impacting shippers who use such routes.
H
- Harbor Maintenance Fee (HMF) – A tax for imported goods collected by the CBP to cover the costs of maintaining and developing U.S. ports and harbors. The rate is based on 0.125% of the commercial value of a shipment.
- Hazmat – An abbreviation for “hazardous materials,” which are substances that can endanger people’s health, safety, and property while being transported or stored.
- High Cube Container (HC) – A shipping container that is one foot taller than a regular container, giving goods more vertical room.
- HTS Code – An acronym for Harmonized Tariff Schedule Code which is a 10-digit number used to categorize imported products and identify the relevant customs duties and taxes.
I
- Importer of Record – A legal entity or individual responsible for making sure that imported goods comply with customs and legal requirements of the importing country, including the filing of paperwork, paying duties and taxes, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Importer Security Filing (ISF) – A document required by CBP for ocean freight imports only that requires importers to provide precise information about their incoming shipments at least 24 hours prior to the departure of the vessel. It is also known as the 10+2.
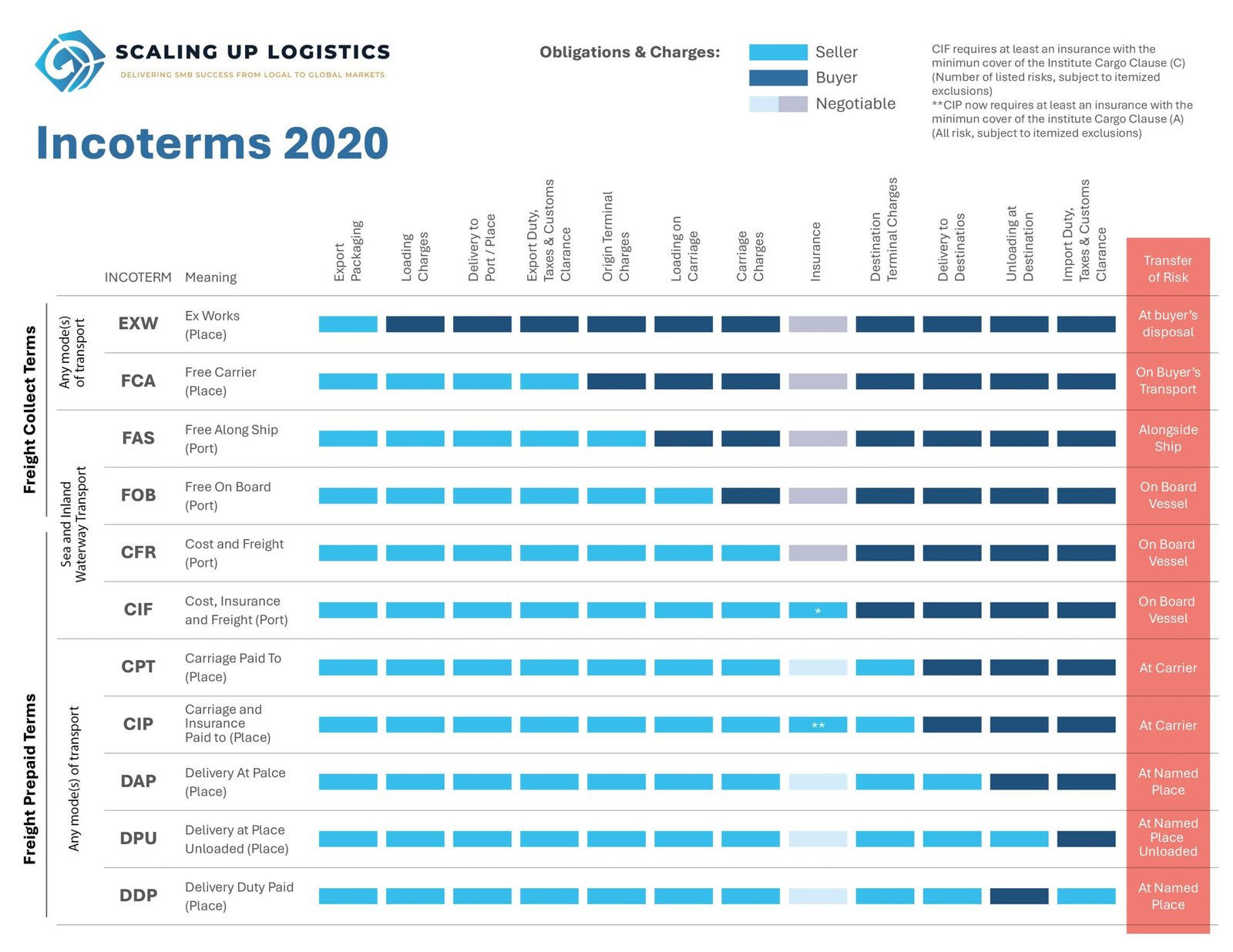
- Incoterms – A collection of internationally accepted trade terms also known as International Commercial Terms, that were created by the International Chamber of Commerce to clarify the responsibilities and obligations of both sellers and buyers in international trade contracts.
- Inside Delivery Fee – An additional charge imposed by the carrier if a shipment needs to be delivered somewhere other than the usual curbside drop-off, like inside a building or to a particular floor due to the extra labor and resources involved.
- Inspection Fee – A term that describes the fees assessed for security checks, screening, and agricultural inspections conducted by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection and other agencies while inspecting cargo.
- Intensive Exam – The most comprehensive customs examination, where the customer bears the cost of having the cargo transported to a Centralized Examination Station (CES) for physical inspection and possible unloading.
- Intermodal Service – A term that describes the movement of goods using two or more modes of transportation, such as truck, rail, and ship, without the goods being touched during the transition between modes inside a container.
- ISF Bond – A financial guarantee required by the CBP that importers will correctly file the necessary paperwork and adhere to ISF requirements when bringing products into the country by sea.
K
- Known Shipper – An individual or business that has been approved by the TSA through a freight forwarder or air carrier to transport goods on both passenger and cargo-only aircrafts.
L
- Lacey Act – A U.S. law created to stop the illegal trafficking of fish, plants, and wildlife. In 2008, it was amended to include plants and plant products, requiring importers to disclose the species and place of origin of plant materials.
- Last Free Day (LFD) – A deadline in shipping and logistics by which a container must be returned to a port or terminal without incurring demurrage or additional storage charges.
- Less than Container Load (LCL) – A less expensive option for lower cargo volume, which is the term for shipping cargo that doesn’t fill a container and is mixed with other shipments in a shared container.
- Less than Truck Load (LTL) – A shipping service in which several small shipments from different businesses are consolidated onto a single trailer.
- Liftgate – A hydraulic platform that is affixed to the back of a truck to facilitate the safe and effective loading or unloading of loads.
- Live Unload – A term that refers to the unloading of a container at the delivery location while the driver is still present, and usually the first 2 hours are free of charge.
M
- Manpower Fee – A term that describes the cost for labor needed for specific tasks, including loading or unloading freight, warehouse functions, or other logistical duties.
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) – A crucial document, now more commonly known as Safety Data Sheet (SDS), that offers comprehensive information about the risks, safe handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals or hazardous materials within a shipment, ensuring safe and compliant transportation.
- Merchandise Processing Fee (MPF) – A tax imposed by the CBP to pay for the expenses of processing and inspecting products entered into the U.S. The rate is based on 0.3465% of the commercial value.
- Messenger Fee – A charge for wiring an electronic check or sending documents to a transportation provider, terminal, or other supply chain partner to release a shipment.
N
- Negotiated Rate Arrangement (NRA) – A written, legally binding agreement between a non-vessel operating common carrier and a shipper establishing specific terms, rates, and services for the transportation of goods.
- Non-Vessel Operating Common Carrier (NVOCC) – An ocean carrier that offers all the services of a carrier but does not own or run its own ships; instead, it leases or purchases space in containers and uses its own House Bill of Lading.
- Notify Party – An entity assigned to receive notifications regarding the status of a cargo, such as arrival notices, customs clearances, and delivery plans, and frequently acting as the point of contact for the carrier.
O
- Original Bill of Lading (OBL) – An essential shipping document that acts as a contract of carriage and a receipt of goods, proving ownership and granting the right to collect the cargo when it arrives at its destination.
- Overweight Fee – An additional cost imposed when a shipment weighs more than the maximum legal weight set by the carrier.
P
- Packing List (PL) – A document for customs clearance and shipment contents verification that lists the items, quantities, and packaging details.
- Pallet – A flat, solid, transportable structure that can carry, store, or transport a load. Usually made of heat-treated wood or plastic.
- Pallet Exchange Fee – A charge by the carrier when a trucker fails to provide pallets to trade during the cargo pickup.
- Particular Average – A term that describes a partial loss or damage to a ship or its cargo that affects only the ship owner or one cargo owner and is not shared by all parties involved.
- Peak Season Surcharge (PSS) – An imposed fee by the shipping lines to offset higher operating expenses and handle capacity limitations during times of high demand, such as holidays or peak shipping periods.
- Per Diem Charge – A penalty cost imposed by shipping lines for keeping a container after it has been unloaded from the vessel for longer than the permitted amount of time.
- Pick Up – The process of collecting goods from a specific place and transporting them to another location.
- Pier Pass – A traffic mitigation fee that is assessed for container movements at the ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach only to encourage cargo movement during off-peak hours in order to reduce congestion and enhance air quality.
- Power of Attorney (POA) – A legal document that gives a freight forwarder or customs broker the authority to act on behalf of a shipper or consignee, allowing them to manage the customs clearance and associated duties and taxes.
- Pre-Pull – A service where a container is picked up from a port and temporarily kept at a trucker’s yard or another storage facility before its scheduled delivery, usually to avoid paying expensive demurrage fees.
R
- Reefer – A specialized container or trailer that has a refrigerator unit to maintain a specific temperature range, which is necessary for moving items that are sensitive to temperature changes.
- Re-weight Fee – An extra cost imposed when a carrier discovers that a shipment’s actual weight deviates from the weight listed on the bill of lading, requiring a re-weighting and probable freight re-classification.
- Roll-On Roll-Off (RORO) – A method of transportation that involves driving cargo, especially cars or other wheeled equipment, directly onto and off a specialized vessel using ramps, eliminating the need for cranes or other lifting equipment.
- Rolled Cargo – Refers to shipments that were scheduled to be loaded onto a ship but were not loaded and instead were rolled to a later sailing, usually as the result of overbooking, space limitations, or prioritization issues.
S
- Schedule B Number – A 10-digit export code used by the U.S. Census Bureau to categorize items exported from the U.S. to facilitate the gathering of trade statistics and export compliance.
- Screening – A term that describes the procedure of examining and assessing cargo to make sure it conforms with safety and security standards using the aid of X-ray machines or explosive trace detection devices.
- Single Entry Bond – A customs bond that ensures the duties, taxes, and fees that will be paid for a single import consignment, which is an affordable choice for infrequent importers whose shipments are low-value.
- Shipper’s Letter of Instructions (SLI) – A document that the exporter fills out, giving the freight forwarder important information and instructions about the shipment, including details of the goods, destination, and any special handling requirements. It also gives the forwarder permission to act on behalf of the shipper.
- Split Shipment – A single order or consignment is split up and sent on different flights instead of arriving on one, usually because of limitations with weight, space, or load planning constraints.
- Spot Rate – A one-time, on-demand freight pricing arrangement that reflects the current market price based on supply and demand, which is subject to quick fluctuations.
- Stop-Off Fee – A charge by the carrier to cover the additional handling and logistics challenges when a shipment needs to make several stops or deliveries to different locations instead of a single destination.
T
- Tailgate Exam – A customs inspection involving the opening of a container and visually inspecting the cargo.
- Tariffs – A government-imposed tax on imported goods significantly impacting the cost and movement of goods across international borders.
- Terminal Handling Charge (THC) – A fee imposed by the terminal for handling the cargo containers, including loading, unloading, storage, and other port activities.
- Triaxle Chassis – A specialized wheeled frame that is used to handle shipments exceeding weight limitations, typically requiring three axles for increased stability and weight distribution.
- Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit (TEU) – A standard unit of measurement used to calculate the cargo capacity of container ships and terminals based on the dimensions of a 20-foot container.
U
- Ultimate Consignee – The company or individual that receives and uses the shipped goods, whether for production, consumption, or resale.
- UN Number – A four-digit code known as the United Nations Number used to identify hazardous goods (hazmat) for international transportation, ensuring safe handling and regulatory compliance.
- Unit Load Device (ULD) – A standardized pallet or container that combines cargo into a single unit for effective airplane loading and unloading to maximize space and boost operational efficiency.
- Unpack & Debris Removal Fee – A service that involves unpacking items after delivery and getting rid of the packaging and any resulting debris. Often part of a white glove service.
V
- Vehicle and Cargo Inspection System (VACIS) Exam Fee – A cost incurred when a shipment is chosen for a non-intrusive X-ray inspection by U.S. Customs to look for contraband or inconsistencies.
W
- Waiting Time Fee – A charge imposed by the carrier when a driver is delayed for longer than a certain allowed time while loading or unloading to make up for the extra time lost as a result of operational inefficiencies.
- Wharfage – A cost assessed by a port authority or terminal operator for the use of their docks or facilities, including loading, unloading, and storing cargo.
- White Glove Service – A premium delivery service marked by careful attention to detail, and personalized care involving unpacking, assembly, installation, and removal of packaging materials.
X
- X-Ray Exam – A customs procedure that involves scanning a container using X-rays to examine its contents to prevent the presence of contraband.
Y
- Yard Storage – The storage of containers in a trucker’s guarded yard when a container cannot be delivered to its final destination.
Incoterms, or International Commercial Terms, are standardized trade terms used in global contracts to define the responsibilities of both the seller (exporter) and the buyer (importer) regarding the delivery of goods.
The International Chamber of Commerce categorizes Incoterms into four groups based on the delivery location of the goods and the specific responsibilities assigned to the seller and buyer.
Group E: Direct delivery at departure
• EXW = Ex-Works
Group F: No payment for main transport
• FCA = Free Carrier
• FAS = Free Alongside Ship
• FOB = Free On Board
Group C: With payment of the main transport
• CFR = Cost and Freight
• CIF = Cost, Insurance, and Freight
• CPT = Carriage Paid To
• CIP = Carriage and Insurance Paid To
Group D: Direct delivery to the point of arrival
• DAP = Delivered At Place
• DPU = Delivered at Place Unloaded
• DDP = Delivered Duty Paid
This classification is updated periodically. The latest version of the Incoterms came into force on 1 January 2020.